FairTrade Coffee
With your cup of coffee in the morning, have you ever wondered how the raw material for the delicious and extremely popular hot drink is actually grown? Then you too belong to a rapidly growing group of coffee lovers, for whom not only outstanding quality and aromatic taste are important when choosing their hot drink, but also fair and sustainable cultivation of the coffee raw material.
Because with a clear conscience, sustainable coffee as a luxury food is given a very special touch that can no longer be imagined in everyday life. We all want to preserve a natural environment for ourselves and future generations that is worth living in. To make this possible, responsible and careful use of the resources available to us are indispensable.
The conscience drinks with many coffee lovers. Most people know that coffee is sometimes produced under inhumane working conditions. The system that carries the “Fairtrade” label seems to be an appropriate answer to this problem. It guarantees small farmers a minimum income. In fact, studies show that the Fairtrade coffee system is often not really fair. Direct Trade allows you to enjoy with a clear conscience.
What Is Fairtrade Coffee?
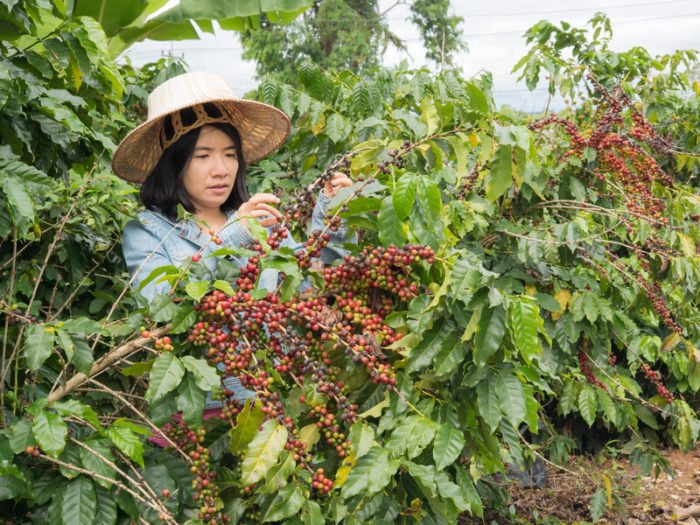

On paper, the system, which is known for its green-blue-black seal of approval, is very well suited to combating abuses in the production of food and beverages in the third world. We cooperate with small farms and in this way support them in a targeted manner. Coffee farmers receive a minimum amount per pound of beans, even if the world price is lower. If the world price is higher, you will receive the corresponding amount. Especially families who want to offer coffee on the world market should be helped in a targeted manner.
Best Coffee Gear Guides

Best Espresso Machines

Best Coffee Makers
Best Coffee Grinders

Best Coffee Beans
Fairtrade Coffee: Not Always Really Fair
The system has various false incentives. If you want to sell your coffee with the “fair” seal of approval, you have to pay an admission fee at the moment. Further annual fees will follow. Many small businesses have to go into debt to do this. As a result, they push down the wages of their employees. The consequence: Scientists from the University of London were able to show that the wages in supposedly “unfair” companies in Uganda or Ethiopia are the same or even higher than in the companies that are allowed to work with the seal.
In addition, it is often not possible to sell the entire production with the seal of approval. And this is where it gets really critical: Suppose a coffee farmer wants to sell two pounds of his beans. With the seal, however, he can only sell half of the goods. The quality from the first pound is very good. For this, he receives 1.50 dollars on the world market. The second pound was unfortunately less successful.
For that, he can redeem only 1.20 dollars on the open market. He, therefore, sells the good coffee beans without a seal, the bad ones with a seal, and receives 1.53 dollars for those through the social supplement. In extreme cases, the system can lead to poorer coffee with a seal coming into circulation – which damages the entire system. Coffee drinkers want to enjoy with a clear conscience – but they also want to enjoy quality coffee.
Does The Money Reach The Farmers?

A study from San Diego shows another critical finding: Americans, for example, would pay 50 cents more per pound of coffee beans that bear the seal in order to help the producers. According to the study, however, this would have little yield. Of every 50 cents, just 0.3 cents actually reach the farmers. The rest of the money is lost along the way.
The organization behind the seal did not want to deal with these criticisms for a long time. According to a report, these points were instead dismissed as “far too generalizing.” At the same time, however, it was admitted that the investigations were not entirely unfounded.
Direct Trade As A Worthwhile Alternative
However, the Fairtrade coffee system is not as bad as the previous lines might make it seem. The minimum price and the social premium are a great relief for many companies. It doesn’t make the market as much better as it claims. But it still makes improvements.
However, there is an alternative that is even more rewarding than Fairtrade coffee in the form of Direct Trade. The intermediate system is omitted here. The sellers in the target countries deal directly with the farmers. They do not have to pay any admission fees.
A corresponding procedure, which is known from the “Coffee Circle” seal, also pays one dollar per pound of social premium. All in all, much more of the money actually reaches the farmers. This also gives them the incentive to really sell their best products to their partners, since they pay the highest sums.
Who benefits from Fairtrade?
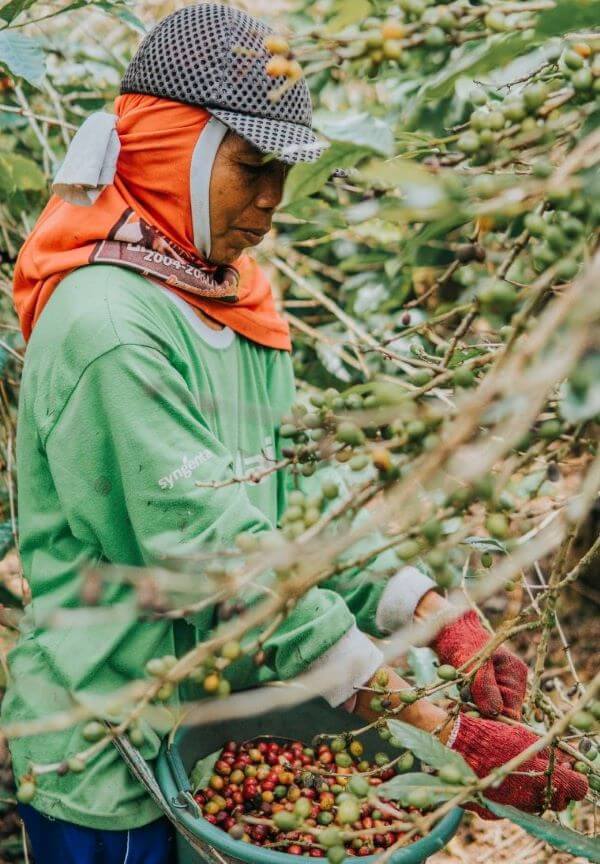

Coffee is one of the most important commodities worldwide. Even if it does not occupy a prominent position as a luxury food in the total trade volume of most importing countries, it dominates the goods exports of many coffee-producing countries. Income from coffee production is therefore not only of great importance for the coffee farmers but for the living conditions of all people in these regions.
Exporting countries can still hardly influence the prices they achieve for their green coffee. There are a number of reasons for this. The most important are:
- Just three major trade organizations handle around 50 percent of all world trade in coffee. They thus have a market power that is overwhelming for coffee producers.
- Between 70 and 80 percent of the coffee grown worldwide comes from small and family farmers. These smallholders are in intense competition with each other. At the same time, they lack a strong lobby and sufficient access to resources and capital.
- Coffee prices are negotiated on international exchanges and are subject to numerous global economic factors. These include, for example, climate change, widespread plant diseases such as coffee rust, rising or falling transport costs worldwide, or currency turbulence. The farmers are also largely powerless in the face of these developments.
Fairtrade International and numerous national initiatives and organizations are working to strengthen the position of coffee farmers vis-à- vis their suppliers and customers and to sustainably improve their living conditions. The word “fair” already signals that charity is not meant as unconditional giving. Rather, it is fair when retailers and consumers recognize the true value that growers create through their hard work.
In addition, the democratic structures of the cooperatives promoted by Fairtrade support the awareness and understanding of democracy in the growing countries. And last but not least, the implemented measures also improve the environmental balance of coffee cultivation and increase yields.
In addition to the small farmers, the entire population of the coffee-producing regions also benefits from Fairtrade. Fairtrade coffee is, therefore, an excellent choice for all lovers of excellent coffee and espresso who care about treating our environment and our fellow human beings responsibly.
The Fairtrade Standards
The goals of Fairtrade are achieved through strict standards that every certified company undertakes to comply with. These standards include:
- Associations of several small farmers to form cooperatives or organizations that sell their coffee and espresso together under more favorable Fairtrade conditions, democratic structures, and political independence of the cooperatives.
- A ban on forced labor and exploitative child labor.
- The sustainable management of coffee-growing areas with environmental standards that limit the use of synthetic fertilizers and pesticides and identify alternatives.
- A fixed minimum price for the green coffee guaranteed by Fairtrade, cushions price slumps on the world market (if the world market price rises above the minimum price, the farmers receive the higher world market price).
- If necessary, pre-financing of the harvest up to 60 percent of the sales price.
- An earmarked Fairtrade premium, with which the cooperatives finance projects to increase quality and productivity as well as social and economic investments.
- An additional premium for organically grown Fairtrade coffee (Although Fairtrade also accepts conventionally grown coffee, the additional premium for organic coffee is motivating more and more coffee farmers to switch their production.).
The farmers and their families benefit from this organizational and financial security
- Social and professional security,
- Reliable foundations for investments and the further development of their operations,
- Better conditions with suppliers and partners,
- Easier access to credit and capital,
- Access to further training and the latest scientific findings on coffee cultivation and harvesting.
In this way, the fairtrade standards create a stable basis for livelihood and a predictable future for countless small businesses in coffee-producing countries.
One Idea Catches On: Fairtrade Coffee
Do you want coffee farmers to be able to make a living from the work of their hands, feed their families, and send their children to school? Do you want to support small cooperatives in competition with international corporations? Then you might opt for Fairtrade coffee. We tell you what you can expect and what you should pay attention to.
Processing Of Fairtrade Coffee

The Fairtrade standards do not contain any regulations for the processing of coffee. However, it is obvious that the green coffee produced in Fairtrade cultivation should be processed just as responsibly. This begins with the manual harvest of the coffee cherries, during which only ripe and flawless fruit is picked. In this way, the coffee farmers ensure that their harvests only contain beans of the highest quality.
Experienced master roasters unlock the aromas of green coffee in a gentle, long-term roasting process at low temperatures. Skilled coffee composers create the finest coffee and espresso blends from the different varieties. And they are finally packaged in packaging that protects the aroma and has as little impact on the environment as possible. Coffee connoisseurs, who reward this care when choosing their favorite coffee with a slightly higher price, support and promote the fair trade idea with every cup of coffee.
Where Does Fairtrade Coffee Come From?
Currently, 730,000 smallholders work on a total of one million hectares of cropland according to Fairtrade standards. The producers have joined together in around 450 producer organizations in all major coffee regions of the world. Latin America and the Caribbean are currently a priority; around three-quarters of all income is generated there. But the number of certified companies is growing all over the world.
Even today, almost every type of coffee or espresso from every growing region in the world is available as Fairtrade coffee. Regardless of where the beans come from and whether they are offered as a single variety or in fine blends: the certificate stands for quality and taste.
However, if you consider that Fairtrade-certified companies have so far only produced a little more than two percent of the total global coffee export, it becomes clear what enormous potential can still be tapped.
Fairtrade Seal Knowledge
There are four seals commonly used on the market to indicate fair trade. In addition to “Coffee Circle” and “Fairtrade”, there is also the red and white “UTZ Certified”, which also sets certain quality standards, and the green and white “Rainforest Seal”, which guarantees particularly ecologically compatible agriculture. The latter are also systems in which the farmers do not deal directly with the sellers.
Fairtrade Coffee - The Solution To All Problems?
Does that mean that coffee drinkers can’t go wrong as long as they choose Fairtrade coffee? Not quite. You can be sure that the certified coffee or espresso comes from plantations where the farmers work under at least acceptable conditions. And they know that Fairtrade International gives these people a fair share of the proceeds from sales to help develop their businesses and their communities.
However, the seal is also awarded to coffee that is not organic guidelines was grown. It does not assess the environmental impact of transport. It says nothing about a more or less gentle roasting of the beans. And in the end, every coffee drinker decides on a coffee or espresso according to their individual taste. Therefore, a Fairtrade seal is not a substitute for your own quality awareness. However, it makes it easier for coffee drinkers to find their way around and shows which coffees they can use to support their producers directly and on-site.
How To Recognize Sustainable Coffee?
Are you now wondering what is the best way to find out whether a coffee blend has been produced sustainably? Well, at first glance the various labels and certificates may seem a bit opaque – but on closer inspection and with a practiced eye it is by no means complicated to find out whether coffee was produced fairly, sustainably, and with direct trade or not.
Everything we consume was once produced by people for people in a specific place at a specific time – that’s clear. The production conditions for coffee are very different depending on the region of origin. The resource-saving handling with water, which of course plays an important role in the cultivation of coffee plants, is one of the aspects on which coffee farmers worldwide focus in order to work sustainably and ecologically.
Such a way of working also includes, among other things, not cultivating the coffee plants in monocultures, as this involves the increased use of plant protection products and insect repellents, which in turn endanger biodiversity. Cultivation in mixed cultures is more sustainable and gentler, for example with an organic seal on the coffee package.
However, not only the cultivation, harvesting, and processing of the coffee beans play a role in the sustainability of the product that we ultimately consume. The packaging material, transport routes, storage, and marketing of the coffee also have an impact on the size of the ecological burden that a coffee ultimately causes.
Many manufacturers therefore no longer only ensure that the coffee beans are grown on-site in a sustainable and ecologically conscious manner, but also pack their coffees, for example from recycled material, for example, and do without prints that are difficult to biodegrade.
How Can I Consume Coffee Sustainably?
From the cultivation to the recycling of coffee, all the intermediate steps are as sustainable as possible fair trade coffee from sustainable cultivation is of course a big step in the right direction when it comes to conscious consumption of the roasts we love so much. But have you ever thought that you can continue to use the coffee powder after it has been prepared as a drink?
Coffee powder is often used in cosmetics, for example peeling. You will find many creative recipes and suggestions for this on various online platforms. As a natural product, the used coffee powder can otherwise be disposed of best and most sustainably in the compost or inorganic waste.
Conclusion: Fairtrade Coffee - Don't Just Trust The Seal

Anyone who drinks coffee with one of the seals is helping to make the market fairer. However, if you want to enjoy with a really good conscience, you should not only trust the seal but also be aware of their weak points – and demand that the systems face the criticism and thus further improve the conditions for the producers.
Disclosure: We use affiliate links in some of the products that appear on this page. This helps our site cover the costs of the site, Thanks for your support. Read more


