Coffee Cultivation - How Does Coffee Grow?
Learn more about optimal coffee cultivation! There are 124 different coffee plants worldwide, with only the two varieties Arabica and Robusta playing a role with a market share of around 96 percent in the global coffee trade. While non-professionals often associate Arabica coffee with high quality and a full flavor, Robusta has fallen into disrepute as an inferior coffee.
However, a hasty generalization does not do justice to the Robusta in particular, after all, coffee lovers can also experience great taste experiences with this variety. Many factors must come together for successful coffee cultivation, which we would like to take a closer look at here. We look at the growing countries, the climatic conditions for good growth, and the trend towards organic farming.
Coffee Cultivation: This Is How The Coffee Beans Grow
Coffee is a bush plant whose seed is around eight weeks old when planted. The coffee bean is freed from its shell and pulp and pressed a few inches into the slightly acidic soil. Five to six weeks later, the freshly grown seedlings can be transplanted into individual containers before being transferred to the plantation with the older plants after another eight months.
The coffee plant grows up to eleven and a half in height but is normally trimmed to around six and a half feet in order to enable the cherries to be harvested by hand and without any additional tools. Around 60 different types of coffee exist worldwide, but only Arabica and Robusta are of particular importance in the overall context of the coffee markets. That is why they are also cultivated the most.
The cultivation of coffee is somewhat similar to that of wine. Both the nature of the soil and the climatic conditions have a decisive effect on the taste of the final product.
Best Coffee Gear Guides

Best Espresso Machines

Best Coffee Makers
Best Coffee Grinders

Best Coffee Beans
Where Does Coffee Grow?
Coffee beans grow in the so-called coffee belt. It is the collective term for tropical countries located on or near the equator. The coffee belt lies between latitude 23 degrees north and latitude 25 degrees south. Here is the perfect, balanced climate for first-class coffee growth.
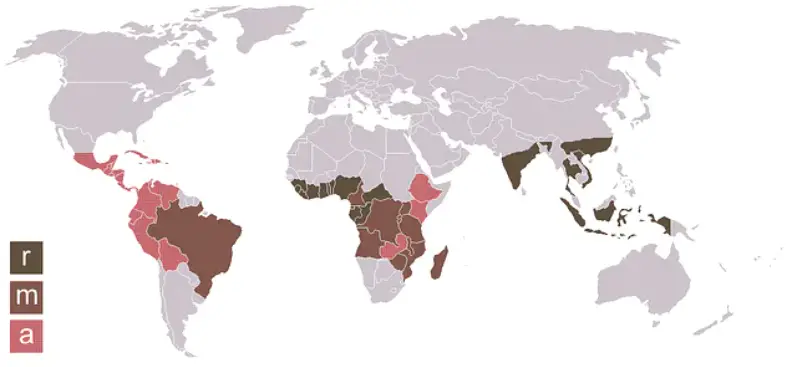
The coffee belt includes many nations in Central and South America, Africa, and also Asia. By far the largest producer from the coffee belt in Brazil. Other major coffee-growing countries are Ethiopia, Colombia, and Indonesia.
Within the regions mentioned, the altitude of the cultivation area has a decisive influence on the maturing time of the coffee. In a mountainous area, for example, the lower temperatures lead to a longer ripening time, while in the lowlands it is exactly the opposite. From an altitude of 3,280 to 6,561 feet, coffee is often referred to as highland coffee. While Robusta, as its name suggests, is more resilient and also grows in the hotter lowlands, Arabica can be found above all from 1,310 to 6,890 feet above sea level.
What Climatic Conditions Does Coffee Need?

Coffee plants need a balanced climate to thrive perfectly. Too much sunshine and temperatures above 86 and below 50 degrees Fahrenheit make the plant suffer and have a negative effect on the harvest. Average annual temperatures of 64 to 77 degrees Fahrenheit are ideal. Coffee finds the best conditions in the coffee belt of the tropics around the equator between 73 degrees north and 77 degrees south latitude.
The world’s largest coffee producers are Brazil, Vietnam, and Indonesia, followed by Colombia, Ethiopia, and Peru. The designations “ highland coffee”, “coffee arabica ” and “ robusta ”.” are not sufficient as a quality designation, rather the cultivation conditions (soil, climate), the time of harvest, the type of processing of the coffee cherries, and the roasting of the beans are decisive for a high-quality product in the end.
How Much Rain Can Coffee Tolerate?
Both too much rain and too long periods of drought are harmful to coffee cultivation. This is a common occurrence in the Guatemalan city of Huehuetenango, where much of the coffee used in Tchibo’s Latin Grande Mix comes from. That is why you will often hear about crop failures in the growing regions in these extreme situations. The annual water requirement per plant is a maximum of 300 ml per cubic foot.
Ideal Humidity And Precipitation
Arabica and Robusta beans love the warm, humid areas around the equator. Arabicas tolerate slightly cooler temperatures as long as the weather remains stable. Its cultivation areas are between 23 degrees north and 25 degrees south latitude, primarily in South America, Africa, Australia, and Indonesia. It is rightly called mountain coffee because it grows in mountainous areas between 3280 and 6560 feet.
Both coffee plants have a water requirement of 250 – 300 mm per cu ft per year. The floor is also subject to high demands. It must be deep, loose, permeable, nutritious, and slightly acidic.
Differences In Varieties
As the name suggests, the Robusta coffee plant is a little more robust than the Arabica coffee plant, it also tolerates slightly higher temperatures and the bean has a higher caffeine content. However, the coffee plant is also sensitive to temperatures above 30 degrees Celsius especially when the humidity is low at the same time.
The Arabica bean, often considered to be of high quality, grows at high altitudes between 1970 and 6890 feet. The Robusta bean, on the other hand, prefers lower altitudes from 0 to 2625 feet above sea level. Robusta also thrives in slightly rainier regions and also grows in very high humidity, while Arabica suffers greatly from warm, humid air and this has a clearly negative effect on crop yields.
Growing Conditions And Harvest

The optimal soils for high-yield coffee growing are deep, loose, well-aerated, and permeable to water. Nitrogen, potassium, and phosphoric acid ensure an ideal supply of nutrients to the plants. In addition, humus-rich soil and a neutral to slightly acidic pH value are beneficial for coffee cultivation. For example, soils with volcanic ash are ideal for growing coffee.
Depending on the growing area and the ripeness of the coffee cherries, the harvest takes place at different times of the year. Since the coffee cherries ripen individually on the bushes, each fruit has a different degree of ripeness. A particularly high-quality raw coffee is produced when coffee farmers harvest the fruit by hand using the so-called picking method.
In contrast to the stripping method of the harvester, which strips off all the cherries from a branch and thus also harvests unripe coffee cherries, the coffee farmer only picks the individual fruits when they are ideally ripe. For cost reasons, such harvesters are often used on large plantations, such as in Brazil or Vietnam, which is why the quality there is often not as high as that of coffee beans from smaller plantations. With the stripping method, the selection process of the coffee cherries is more important than the picking method. In addition, the waste with the stripping method is significantly higher, since a comparatively large number of unripe fruits are harvested.
The picking method, on the other hand, is much more time-consuming and is being used less and less against the background of increasing intensification of industrial coffee production. After harvesting, the coffee cherries are dried and processed, then the pulp, the mucus layer, and the parchment skin are removed from each bean and, if necessary, further drying is carried out. The dried beans are filled into sacks and usually shipped in the unroasted state
Other Climatic Factors
Since coffee belongs to the nightshade family, the plant prefers a shady place. This is precisely why coffee is often grown next to other plants or on mountainous slopes to avoid the sun. In addition to the sun, the wind also becomes a lesser factor. In order to achieve the desired growth, coffee plants need a variety of nutrients. These are mainly found in soils of volcanic origin within the coffee belt.
Climate Change And Coffee Cultivation

Coffee producers are hit particularly hard by the effects of climate change. The plants are very sensitive and have very specific requirements in terms of temperatures, humidity, soil conditions, and rainfall. Higher temperatures primarily affect Arabica, while the temperature fluctuations associated with climate change primarily affect Robusta. Experts expect that in Brazil, in particular, many areas under cultivation will disappear in the coming decades and cannot be compensated for by new developments in the country.
Instead, the focus is on new cultivation areas in East Africa and Southeast Asia, where coffee cultivation has not previously been worthwhile. However, it is questionable how the new areas can be developed sustainably. While in East Africa the development appears to be quite unproblematic, many cultivated areas in Southeast Asia are covered by rainforest. Extensive deforestation would have fatal consequences for ecosystems and would further accelerate climate change. On the other hand, there is an ever-increasing demand for coffee worldwide, which the producers have to meet.
Sustainable Cultivation Of Coffee
The sustainability aspect in the cultivation of coffee has many reasons. Since coffee only grows in subtropical and tropical areas, it is an important reason for the displacement of the rain forest, in which it is in direct competition. The leaching of the soil means that it can then usually only be used for grazing cattle. In addition, chemical fertilizers and pesticides are often used to avoid pests. They also migrate into the soil and with it the groundwater.
Protecting the environment is the goal of organic farming. Above all, he avoids the use of pesticides and genetic engineering. While organic coffee is mostly loss-making in the short term, it is profitable in the long run. This is mainly due to the fact that the soil can be used much longer than before and biodiversity is less affected.
In addition to ecological sustainability, the focus is also on social responsibility. Organizations like Fairtrade want to ensure that coffee farmers receive socially fair conditions to do their work. This includes, for example, fixed wages, avoiding indebtedness to loan sharks, and material help within the community, for example by building schools. More and more people are supporting the fundamentally good idea of sustainable cultivation by buying coffee with the Fairtrade seal. However, there is the disadvantage that they do not receive all the information and no insight into the living conditions on-site, which are often very bad despite the organic seal and the like.
When And How Does The Coffee Harvest Take Place?
The coffee harvest is the final step of growing cherries. It depends on the right time, which differs depending on the location, the climate, precipitation, and the hemisphere. So while Guatemala harvests from November to March, Brazil harvests between April and September. The coffee cherries must be red to harvest in order to get the typical aromatic taste.
Conclusion
Coffee is the second most important commodity in the world after crude oil and plays a major role in international trade. The cultivation of the plants, which is subject to very specific climatic conditions in order to be successful, is of corresponding importance.
The most important part of coffee cultivation takes place in the so-called coffee belt, which is located along the equator and includes various continents. It is a very exciting region that is responsible for all the coffee in the world. Given the spatial limitations of the area, the most important thing is to ensure that it is grown as sustainably as possible so that you can continue to enjoy your favorite coffee in the future.
Coffee plants are sensitive and make comparatively high demands on their environmental conditions for optimal growth. So that coffee lovers can ultimately hold a perfect bean in their hands, the climatic conditions, the soil conditions, the time of harvest, the processing, and the roasting are particularly important.
Coffee plants only thrive near the equator because they need temperatures of at least 55 degrees and a maximum of 86 degrees. The soils must be deep, loose, well-aerated, and permeable to water. Nitrogen, potassium, and phosphoric acid provide the plants with nutrients. Climate change and an increasing global coffee demand are the most important challenges for future coffee cultivation.
Disclosure: We use affiliate links in some of the products that appear on this page. This helps our site cover the costs of the site, Thanks for your support. Read more